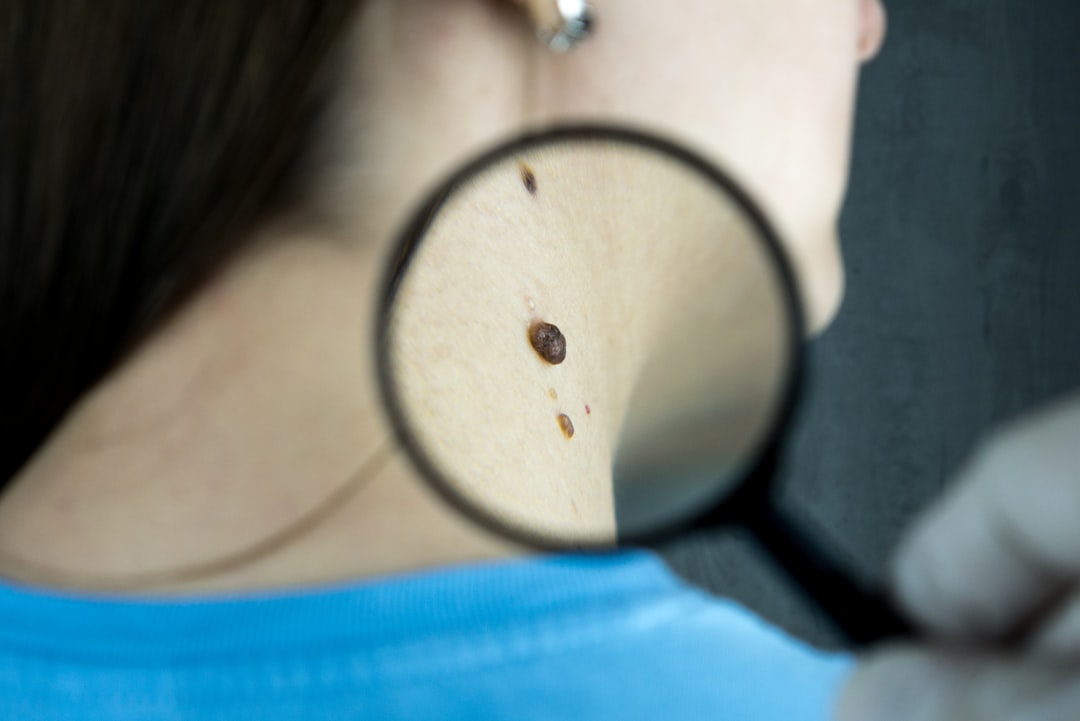
Melanoma sun spots, also known as skin moles or nevi, are pigmented spots on the skin that can develop into melanoma, a type of skin cancer. These sun spots are caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. While most sun spots are harmless, some can become cancerous if not properly monitored and treated. It is important to understand the characteristics of melanoma sun spots in order to recognize and address any potential issues.
Melanoma sun spots can develop anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on areas that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs. These spots can vary in size, shape, and color, and may be flat or raised. It is important to monitor any changes in sun spots, as this can be an indication of melanoma development. Understanding the potential risks and characteristics of melanoma sun spots is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Melanoma sun spots are caused by an overproduction of melanin in the skin due to sun exposure.
- It is important to recognize the ABCDEs of melanoma: asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter larger than a pencil eraser, and evolving size, shape, or color.
- Common signs of melanoma sun spots include changes in size, shape, or color, itching, bleeding, and tenderness.
- Differentiating between benign and malignant sun spots requires professional evaluation, including a biopsy if necessary.
- Seeking professional help for suspicious sun spots is crucial for early detection and treatment of melanoma.
- Self-examinations can be used to monitor sun spots for any changes in size, shape, or color.
- Preventing and protecting against melanoma sun spots involves using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours.
Recognizing the ABCDEs of Melanoma
When examining sun spots for potential melanoma, it is important to be aware of the ABCDEs of melanoma. These are key characteristics to look for when assessing the risk of a sun spot becoming cancerous. The ABCDEs stand for asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter, and evolution.
Asymmetry refers to the shape of the sun spot. If one half of the spot does not match the other half, it may be a cause for concern. Border irregularity refers to the edges of the spot. If the borders are not well-defined or appear jagged, it could be a sign of melanoma. Color variation refers to the different shades of color within the spot. If there are multiple colors present, such as brown, black, red, white, or blue, it may indicate a potential issue. Diameter refers to the size of the spot. If it is larger than a pencil eraser (6mm), it should be monitored closely. Evolution refers to any changes in the spot over time. If there are any changes in size, shape, color, or elevation, it is important to seek medical attention.
Understanding and recognizing the ABCDEs of melanoma is crucial for early detection and treatment of potentially cancerous sun spots. By being aware of these key characteristics, individuals can take proactive measures to monitor and address any suspicious sun spots.
Identifying Common Signs of Melanoma Sun Spots
In addition to the ABCDEs of melanoma, there are other common signs and symptoms to look for when identifying potential melanoma sun spots. These signs can help individuals determine whether a sun spot may be cause for concern and require further evaluation by a medical professional.
One common sign of melanoma sun spots is itching or tenderness. If a sun spot becomes itchy or painful, it may be a sign of abnormal cell growth and should be examined by a dermatologist. Another sign to look for is bleeding or oozing from the sun spot. Any unusual discharge from a sun spot should be addressed promptly to rule out any potential issues.
Changes in the texture of a sun spot can also be a cause for concern. If a sun spot becomes scaly, rough, or begins to crust over, it may indicate abnormal cell growth and should be evaluated by a medical professional. Additionally, any sun spot that appears to be growing rapidly or has an irregular shape should be monitored closely.
By being aware of these common signs and symptoms of melanoma sun spots, individuals can take proactive measures to monitor their skin health and seek medical attention if necessary.
Differentiating Between Benign and Malignant Sun Spots
| Feature | Benign Sun Spots | Malignant Sun Spots |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small to medium | Large |
| Shape | Regular and symmetrical | Irregular and asymmetrical |
| Color | Uniform color | Varied color with dark spots |
| Border | Smooth and well-defined | Irregular and blurred |
| Changes over time | Stable or slow changes | Rapid changes in size, shape, or color |
Differentiating between benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) sun spots is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. While most sun spots are harmless, some can develop into melanoma if not properly monitored and addressed. Understanding the key differences between benign and malignant sun spots can help individuals take proactive measures to protect their skin health.
Benign sun spots are typically uniform in color and shape, with well-defined borders. They are usually small in size and do not change significantly over time. These spots are generally harmless and do not require medical intervention unless they become bothersome or cosmetically undesirable.
Malignant sun spots, on the other hand, often exhibit irregularities in color, shape, and size. They may have asymmetrical borders and can change in appearance over time. Malignant sun spots may also exhibit itching, tenderness, bleeding, or oozing. It is important to seek medical attention if any of these signs are present in order to rule out potential melanoma development.
By understanding the key differences between benign and malignant sun spots, individuals can take proactive measures to monitor their skin health and seek medical attention if necessary.
Seeking Professional Help for Suspicious Sun Spots
If an individual notices any suspicious signs or changes in their sun spots, it is important to seek professional help from a dermatologist or healthcare provider. Early detection and treatment of potential melanoma sun spots is crucial for successful outcomes and skin health.
A dermatologist can perform a thorough examination of the sun spot and determine whether further testing or treatment is necessary. This may include a skin biopsy to analyze the cells within the spot and determine if they are cancerous. If melanoma is detected, the dermatologist can develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
In addition to seeking professional help for suspicious sun spots, individuals should also communicate any concerns or changes in their skin with their healthcare provider during regular check-ups. This open dialogue can help ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly and effectively.
By seeking professional help for suspicious sun spots, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their skin health and address any potential concerns in a timely manner.
Using Self-Examinations to Monitor Sun Spots

Regular self-examinations are an important part of monitoring sun spots for potential melanoma development. By performing self-examinations on a monthly basis, individuals can become familiar with their skin and identify any changes in their sun spots that may require further evaluation.
When performing a self-examination, it is important to thoroughly inspect all areas of the body for any new or changing sun spots. This includes using a mirror to examine hard-to-see areas such as the back, scalp, and buttocks. It is also important to pay attention to any changes in existing sun spots, such as size, shape, color, or texture.
If any suspicious changes are noted during a self-examination, it is important to seek professional help from a dermatologist or healthcare provider for further evaluation. Early detection and treatment of potential melanoma sun spots is crucial for successful outcomes and skin health.
By using self-examinations to monitor sun spots, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their skin health and address any potential concerns in a timely manner.
Preventing and Protecting Against Melanoma Sun Spots
Preventing and protecting against melanoma sun spots is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin cancer. There are several proactive measures that individuals can take to protect their skin from harmful UV radiation and reduce the risk of developing melanoma sun spots.
One key preventive measure is to limit exposure to direct sunlight during peak hours (10am-4pm) when UV radiation is strongest. This can be achieved by seeking shade, wearing protective clothing such as hats and long sleeves, and using sunscreen with a high SPF rating.
It is also important to regularly apply sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection (UVA/UVB) to all exposed areas of the skin, including the face, neck, arms, and legs. Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours or after swimming or sweating to ensure maximum protection.
In addition to these preventive measures, individuals should avoid indoor tanning beds and booths, as they emit harmful UV radiation that can increase the risk of developing melanoma sun spots.
By taking proactive measures to prevent and protect against melanoma sun spots, individuals can reduce their risk of developing skin cancer and maintain healthy skin for years to come.
In conclusion, understanding melanoma sun spots and taking proactive measures to monitor and protect against them is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin cancer. By recognizing the ABCDEs of melanoma and common signs of potential issues, individuals can take proactive measures to seek professional help when necessary. Regular self-examinations and preventive measures such as sunscreen use and UV protection are also important components of maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of developing melanoma sun spots. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, individuals can protect their skin health and reduce the risk of developing melanoma sun spots.
If you’re concerned about sun spots on your skin, you may want to read this article on melanoma and skin cancer prevention. It provides valuable information on how to protect your skin from harmful UV rays and reduce your risk of developing melanoma. Taking proactive steps to protect your skin is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing serious skin conditions.
FAQs
What are melanoma sun spots on skin?
Melanoma sun spots on the skin are areas of pigmentation that develop as a result of sun exposure. They are also known as solar lentigines or sun-induced freckles.
What causes melanoma sun spots on skin?
Melanoma sun spots on the skin are caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. This exposure can lead to an increase in melanin production, resulting in the formation of sun spots.
Are melanoma sun spots on skin dangerous?
While most melanoma sun spots on the skin are harmless, they can sometimes be a sign of skin damage and an increased risk of skin cancer, including melanoma. It is important to monitor any changes in sun spots and seek medical attention if there are any concerns.
How can melanoma sun spots on skin be prevented?
Melanoma sun spots on the skin can be prevented by practicing sun safety measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours. It is also important to avoid tanning beds and sunlamps.
How are melanoma sun spots on skin treated?
Treatment for melanoma sun spots on the skin may include topical creams, laser therapy, or cryotherapy to reduce the appearance of the spots. In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend monitoring the spots for any changes or performing a biopsy to rule out skin cancer.